Introduction
A tumor is a lump that can grow in different parts of the body. Tumors in the nose and sinuses are uncommon, making up less than 1% of all tumors. These growths can be either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). They come in various sizes, types, and locations. Treating patients with these tumors requires a personalized approach involving different medical experts. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, either alone or combined.
Symptoms
The signs of nasal and sinus tumors are not specific and can be hard to tell apart from other common nasal issues like allergies or sinus infections. Symptoms may include stuffy nose, facial pain and pressure, a runny nose, and mucus dripping down the throat. More worrisome symptoms might include repeated or severe nosebleeds, swelling of the face, changes in vision, watery eyes, and numbness in the face. Symptoms that only occur on one side or get worse over time can also be concerning. And if these symptoms start in older people for the first time, it raises concerns for a tumor. Ultimately, diagnosing nasal tumors requires evaluation by a specialist.
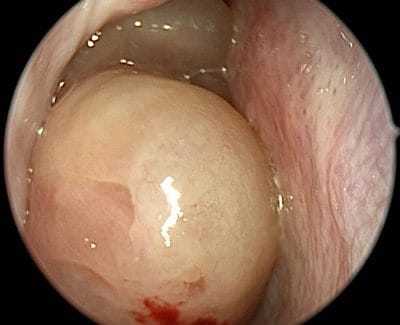
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose nasal and sinus issues, including tumors, with the help of an ear, nose, and throat specialist (ENT). They start by asking about symptoms and examining the head and neck. They may also use a small tool with a camera called an endoscope to look inside the nose. If a tumor is suspected, imaging tests like CT scans, MRI scans, or PET-CT scans are done. These tests help doctors see the tumor and understand its nature. A biopsy, which involves taking a small tissue sample, may also be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Types of Tumors
There are different types of both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) tumors that can develop in the nose and sinuses. Benign tumors, though not cancerous, can still cause problems as they grow. They include various types like papillomas, fibro-osseous tumors, vascular tumors, and neurogenic tumors, among others. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, are typically more aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body. They include types like squamous cell carcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma, adenocarcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, melanoma, and lymphoma, among others.
Treatment Options
Treating nasal tumors, whether benign or malignant, is complex and involves multiple medical specialties. Treatment decisions depend on factors like the patient’s overall health, the type and location of the tumor, and how far it has spread. Treatment can involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Most benign tumors are treated with surgery alone, while treatment for malignant tumors often requires a combination of therapies.
Surgery for Nasal Tumors
Surgery for nasal tumors can be done in different ways. There’s “open surgery,” which involves making cuts on the face and scalp, and “endoscopic surgery,” which uses a small camera to remove the tumor through the nostrils. Endoscopic surgery has benefits like avoiding visible scars and providing better visibility for the surgeon. The choice of surgery depends on the patient’s needs and the extent of the tumor. These surgeries are complex and may involve a team of specialists, including ENT and neurosurgery.
Steps of Surgery
Surgical treatment involves several steps. First is the planning phase, where the patient and the medical team discuss the treatment plan. Then comes the surgery itself, which involves removing the tumor and reconstructing the affected area. Finally, there’s the postoperative care, which includes recovery, additional treatment like radiation or chemotherapy, and long-term follow-up to monitor for any recurrence or complications.